Shop by Industry
Industries we support...
Products
START SHOPPING...
EXPLORE by category
Product Series
Resources
Contact
Find a Dealer
Infrared light is all around us. We use it in our home security cameras, it can help heal skin and muscles, firefighters use it as a secret weapon to fight fires, and law enforcement and military units use it for special operations. But what exactly is this invisible infrared light?
Infrared light(IR) is a longer wavelength electromagnetic radiation that falls outside the visible light spectrum. IR wavelengths measure between 700 and 14,000 nanometers(nm). For reference, the visible spectrum of light is 400-700nm, and UV light is 10-400nm.
Infrared is visible to the naked eye up to around 850nm and appears as a faint deep red/purple glow. IR becomes invisible to the naked eye above 850nm.
| Type | Range | Application |
| Near-infrared | 750-1400 nm | Forensic, night vision |
| Short wavelength infrared | 1400-3000 nm | Long-range telecommunications |
| Med-wavelength infrared | 3000-8000 nm | Thermal infrared, military aircraft tracking |
| Long-wavelength infrared | 8000-14000 nm | Thermal imaging or thermography |
Infrared is used for various applications ranging from skin therapy, night vision, telecommunications to thermal imaging. This article will focus on near-infrared wavelength (750-1400nm) light and its uses for public safety applications.
IR light around 940nm is used as active illuminator light for night vision devices or goggles. At 940nm, the light is invisible by the naked eye, making it ideal for tactical applications like SWAT, special ops, and border security.
Night vision devices or goggles work by gathering existing ambient light. This light, which is made up of photons, is converted to electrons. The electrons are then amplified to a much greater number. The amplified electrons are then converted into visible light on a screen, resulting in a relatively bright image otherwise invisible to the naked eye. (Credit: ATN)
When 940nm infrared light illuminates the night vision device scene, the image is brighter and clearer for the operator to see.
Forensic investigators use IR light in the 750-850nm range for several applications.


While thermography doesn't require extra infrared light, it's good to understand the difference between long-wavelength infrared and near-infrared.
Thermal imaging or thermography is different than night vision. Unlike NVDs that alter photons and electrons to create a visible image, thermal imaging measures the radiation(heat) emitting from a subject. A thermal imaging camera reads the radiation based on emissivity and then displays the image's different temperature levels.
Thermography is a common tool for firefighting. A thermal camera highlights the heat signature behind a wall or a roof by identifying the increased temperature of the structure's exterior. This is beneficial in determining where and how fire is traveling within a structure.
Thermal cameras are also used in search and rescue for identifying lost persons in the forest or wilderness. The thermal camera displays a bright color contrast of the victim's heat signature, making it easier to identify a victim lost in the woods. Thermal cameras are especially beneficial if the victim is in a forest under a canopy of leaves. Their heat signature may be more visible than the view through a regular camera or scope.
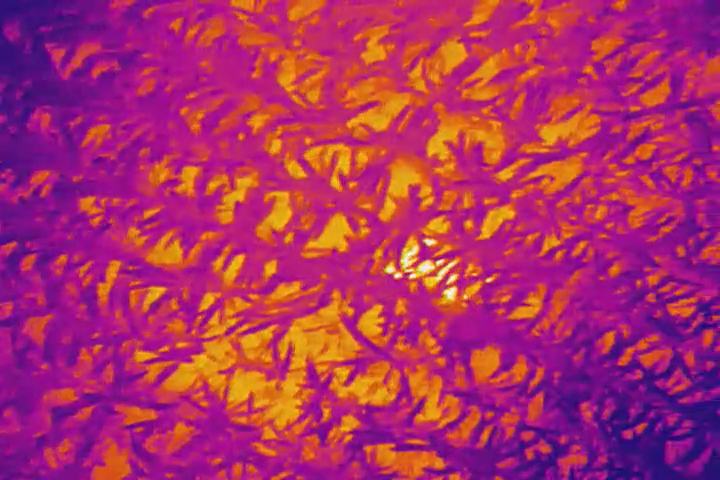
Infrared light opens up a whole new world of possibilities for law enforcement and first responders. It's essential to understand what your needs are when using infrared light.
Key facts to remember – 850nm helps identify bruising and abuse for forensics, and 940nm is ideal for illuminating night vision devices and goggles.
Visit FoxFury to see all of our tactical and forensic infrared lighting solutions.


Enter your details below to save your shopping cart for later.